Note | Constraint Satisfaction Problem
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Week 6 Notes
CSPs Introduction
Constraint Satisfaction Problem 其定義為一組物件,而這些物件需要滿足一定的限制或條件,而這個問題可能有很多的解。CSP 問題經常表現出高複雜性,需要結合啟發式搜尋和搜尋方法來在一個合理的時間內解決問題。
主要解法:通過識別違反約束的變量與值的組合消除大規模的搜索空間。
- CSP related
- Linear programming
- Nonlinear progaramming
- Numerical analysis
- CSP application
- Operations research
- Network flows
- optimization problems
CSP Define
定義一個 3-tuple(X, D, C) 其中
X = {X1, …, Xn} Finite set of variables.
D = {D1, …, Dn} Nonempty domain of possible values for each variable.
C = {C1, …, Cn} Finite set of constraints, Each constraint Ci limits the values that variables can take.
Example
Map coloring 就是一個經典的 CSP。每個區域即是變數,顏色便是值域,相鄰區域顏色不同是約束。
其中關於 Constraint 可被劃分為:
- unary constraint: 只約束單個 variable 的取值。如 SA 不能被染成綠色。
- binary constraint: 兩個 variable 相關的約束。如 SA 不能與 WA 的顏色相同。
- global constraint: 全局約束。如 Alldiff, 即約束中所有 variable 皆需取不同的值。

Arc Consistency example
Backtracking search for CSPs
回朔搜索,用於 DFS 中。他每次為 Single variable 進行取值,當沒有合法的值可給某個 variable 時就進行回朔。
- 為使 search 變的高效,須解決以下問題:
- 下一步應該給哪個 variable 取值? 按照什麼順序取值?
- 每步 search 應該做怎樣的推理?
Variable select: Minimum remaining values (MRV)
最少剩餘值啟發式: 選擇合法取值最少的 variable 開始。這樣選擇的 variable 可能很快地導致失敗,從而進行回朔。
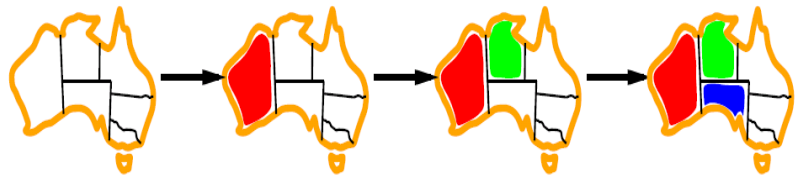
Degree heuristic
鄰接度啟發式: 選擇與其他未取值 variable 約束最多的 variable 來試圖降低未來可能的分支。

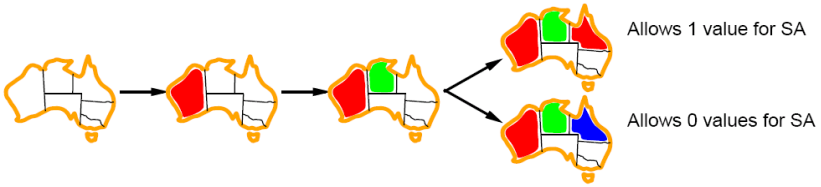
Value order
Least constraining value (最少限制值): 選擇 value 時優先選擇給鄰居 variable 留下最多選擇的分支。
Inference in CSPs
在 CSP 問題中,Algorithm 可以進行搜索,也可以做約束傳播 (The constraint propagation) 的推理
約束傳播: 使用約束來減少一個 variable 的合法取值範圍,從而影響與此 variable 有約束關係的另一個 variable 的取值。 (局部相容性)
Node Consistency (節點相容)
Single variable (In CSP Single node) 值域中的所有取值滿足他的 unary constraint.
if SA = NA = {Red, Blue, Green};
SA != Blue, NA != Red, SA = {Green, Red}, NA = {Blue, Green};
Arc Consistency (弧相容)
CSP 中某 variable range 所有取值滿足該 variable 的所有 binary constraint.
最常用的算法為 AC-3, 算法流程大致如下:
- Get all the constraint and turn each one into two arcs.
Expmale: A > B becomes A > B and B < A.- Add all the arcs to a queue.
- Repeat until the queue is empty:
3.1. Take the first arc (𝑥, 𝑦), off the queue (dequeue).
3.2. For every value in the 𝑥 domain, there must be some value of the 𝑦 domain.
3.3. Make 𝑥 arc consistent with 𝑦. To do so, remove values from 𝑥 domain for which there is no possible corresponding value for 𝑦 domain.
3.4. If the 𝑥 domain has changed, add all arcs of the form (𝑘, 𝑥) to the queue (enqueue). Here 𝑘 is another variable different from 𝑦 that has a relation to 𝑥.
Forward Checking
向前檢驗是最簡單的推理形式,只要 X variable 被賦值了,就向前檢驗過程對他做 Arc Consistency. 檢查對於每個通過約束與 X 相關的, 未賦予值的 Y variable, 從 Y 的 range 中消去與 X 不相容的值。
NOTE
待更新